Don Norman’s JND.org. (2023). About Don Norman. [online] Available at: https://jnd.org/about-don-norman/about-don-norman/.
Sirk, C. (2019). The Godfather of UX: Don Norman & User-Centered Design. [online] CRM.org. Available at: https://crm.org/articles/the-godfather-of-ux-don-norman-user-centered-design.
prabook.com. (n.d.). Donald Arthur Norman. [online] Available at: https://prabook.com/web/donald_arthur.norman/1701633 [Accessed 3 Jan. 2024].
www.designprinciplesftw.com. (n.d.). Don Norman | Design Principles FTW. [online] Available at: https://www.designprinciplesftw.com/authors/don-norman.
www.cs.york.ac.uk. (n.d.). Professor Don Norman - Computer Science, University of York. [online] Available at: https://www.cs.york.ac.uk/equality-and-diversity/heroes-of-computer-science/professordonnorman/ [Accessed 3 Jan. 2024].
Batterbee, I. (2020). Don Norman’s seven fundamental design principles. [online] Medium. Available at: https://uxdesign.cc/ux-psychology-principles-seven-fundamental-design-principles-39c420a05f84.
www.designprinciplesftw.com. (n.d.). Don Norman | Design Principles FTW. [online] Available at: https://www.designprinciplesftw.com/authors/don-norman [Accessed 12 Dec. 2023].

Design Principles
"How has Don Norman's design philosophy influenced design practices and the user experience?”
by Harry Craig
Finlayson, C. (2020). Affordance: The Indicator of Good Design. [online] Medium. Available at: https://medium.com/@thoughtbottler/affordance-the-indicator-of-good-design-1977362f4ea9.
Introduction
Introduction
Design Principles
Don Norman has various approaches to design practice and user experience; he has six core principles that he uses. The first principle is visibility, this is crucial in design as users of different products must be able to see and understand different function on a platform. Interfaces must be intuitive and easy to use, if they are not then significant functionality is lost.
His second principle is feedback to users, allowing them to understand the consequences of their actions. This principle has led to the integration of visible and immediate feedback mechanisms in user interfaces, contributing to a more transparent and user-friendly experience. feedback is also a massive part of user experience as it gives designers help if the users of the product or interface tell them what needs to be fixed or adjusted through different methods like verbal or tactile feedback.
The third principle is constraints, this can be very important as UX designers will have to follow constraints so that the user gets the best possible outcome.
Don Normans fourth principle is mapping which needs to be implemented so that the website or platform can be used by various methods for example mouse or arrow keys and mapping is also crucial for usability so that everyone will be able to use the product provided.
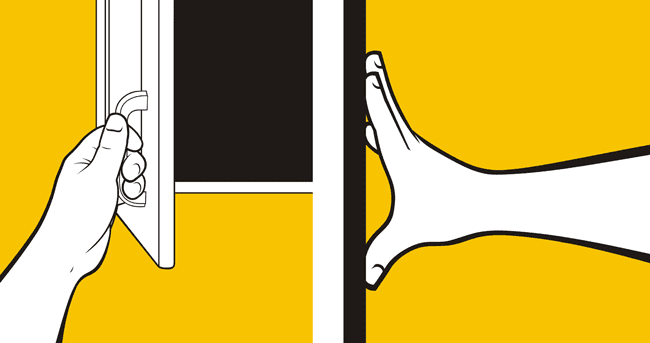
The fifth principle of design is Affordance which is a design concept that James J. Gibson created in 1979. This concept in design is very important for users, as designers must try to make products that users can use instinctively without thinking how to use the specific object or product. Apple is particularly good at using affordances in their devices for example IOS is extremely intuitive compared to other mobile operating systems and even with devices like air pods as its obvious that the only way to use them is as earphones.
The sixth and last of Don Norman’s design principles is consistency, products and websites must utilise a consistent design so that it looks cohesive and so that the user doesn’t get frustrated or thrown off by the sudden lack of consistency.
“An affordance is a relationship between the visual cues provided by an object and the capabilities of a person, which determine how said object could be used.”
Nielsen Norman Group. (2018). Don Norman, co-founder and principal of Nielsen Norman Group. [online] Available at: https://www.nngroup.com/people/don-norman/.
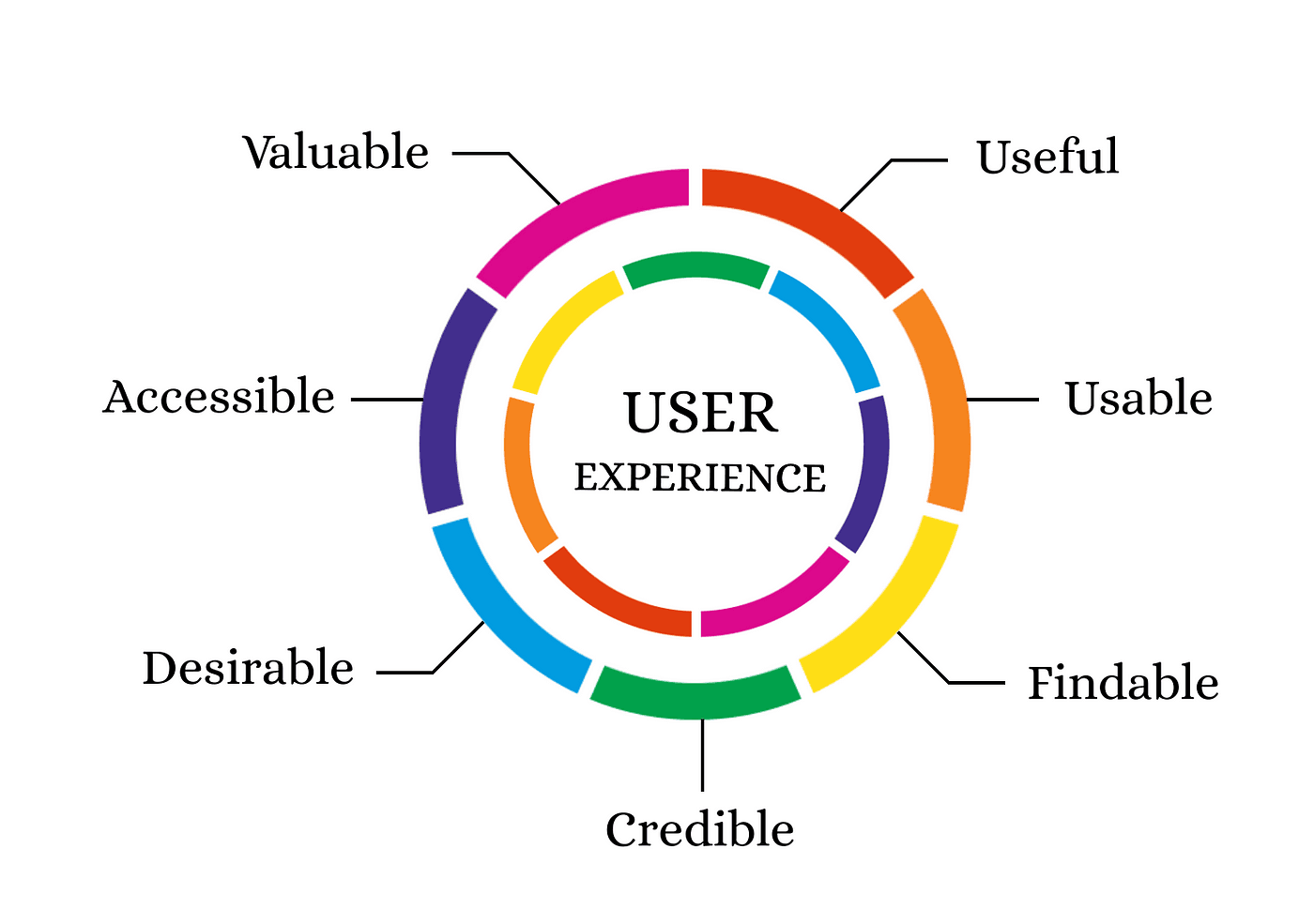
User Experience
Don Norman is an American designer, author and professor, Norman was born on December 25th 1935, in New York City, He has a degree in electrical engineering from MIT and a PhD in psychology from the university of Pennsylvania. After his studies he became a lecturer at Harvard and after four years Norman left to become an associate professor at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD). In 1993 he left UCSD to become a fellow at apple then later becoming the first user experience designer, following his career at apple he co-founded Nielsen Norman group in 1998 which is an user interface and experience consulting firm. Throughout his career Norman wrote fifteen books on a variety of different subjects including design and psychology.

User - Experience
Don Norman throughout his career as an author and designer has made significant impacts within the design and user experience world with his books on design: “The design of everyday things” and “emotional design why we love (or hate) everyday things” which have changed the way that user experience designers approach the work they haven and how people view the work of UX and UI designers.
Within the Design sector Don Norman is a key figure as a result of his work, in 1988 he published the book “The Design of Everyday Things” it covered User-Centered Design, a concept he helped popularize, involves placing the user at the center of the design process. This approach ensures that products and systems are created with a deep understanding of user behaviors', preferences, and limitations, leading to more intuitive and user-friendly designs. was a precursor to UX (User Experience) this book was also the first to cover UX which focused more on what the user wanted rather than the look or design of the system. Norman joined apple in 1993 where he eventually became the first user experience designer.
“Design is really an act of communication, which means having a deep understanding of the person with whom the designer is communicating.”― Donald A. Norman,
www.goodreads.com. (n.d.). Donald A. Norman Quotes (Author of The Design of Everyday Things). [online] Available at: https://www.goodreads.com/author/quotes/552.Donald_A_Norman.
Principles of design
7. When all else fails, standardize.
6. Design for error.
5. Exploit the power of constraints.
4. Get the mappings right.
3. Make things visible: bridge gulfs between Execution and Evaluation.
2. Simplify the structure of tasks.
1. Use both knowledge in the world and knowledge in the head.
Conclusion
Conclusion
in conclusion, Don Norman's design philosophy has left a mark on the world of design, revolutionizing practices and shaping the user experience across various fields. By helping User-Centered Design become widespread, introducing concepts like affordances and signifiers, and for consideration of emotional and human factors, Norman has guided designers toward creating products and interfaces that are not only functional but also deeply intuitive and user-friendly.
The influence of Norman's ideas is evident in design principles such as feedback and visibility, error prevention and recovery. As technology continues to advance, his emphasis on human-centered technology remains relevant, urging designers to create systems that adapt to human capabilities rather than demanding users adapt to technological constraints.
Don Norman's design philosophy has sparked a shift, encouraging designers to think beyond usability and functionality. It has prompted a consideration of the emotional impact of design and a commitment to creating products that resonate with users. As design continues to grow in the computing world, the legacy of Don Norman continues to inspire a generation of designers to prioritize the user experience, innovation and improvements that enhance the way we interact with the world around us.


References
Books
Books
Don Norman's design books have been very important in shaping the philosophy and practice of design, significantly impacting user experiences across the world.
"The Design of Everyday Things" introduces the concept of user-centered design and emphasises the importance of intuitive interfaces.
Norman's second book on design is "Emotional Design why we love (or hate) everyday things". He introduces behavioural levels of design he also explains the significance of aesthetics. This extensive approach encourages designers to go beyond functionality, crafting products that make positive emotional responses and create lasting connections with users.
These books form a comprehensive framework for designers, offering guidance and foundation. Norman's contributions have made design more widespread, emphasizing not only the functional aspects but also the emotional and dimensions that define user experience. His books continue to help designers create great and meaningful pieces of work.